DNA, chromosomes and genesDNA is
short for DeoxyriboNucleic Acid and is a molecule that contains the entire set
of hereditary material of humans and almost all other organisms.
DNA lives in the cells and nearly every cell in a person's body has the same DNA. The information in DNA is stored as a code made up of four chemical bases: adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G) and thymine (T). The order of these bases determines the information available for building an maintaining an organism. This is similar to the way in which letters of an alphabet appear in a certain order to form words and sentences. DNA bases pair up with each other, A with T and C with G, to form units called base pairs. To each base is attached a sugar molecule and a phosphate molecule and together this forms a nucleic acid or nucleotide. Nucleotides are arranged in long strings that form a spiral called a double helix and this is our DNA. DNA looks a bit like a twisted ladder, in which the base pairs form the ladder's rungs and the sugar and phosphate molecules form the vertical sidepieces of the ladder. 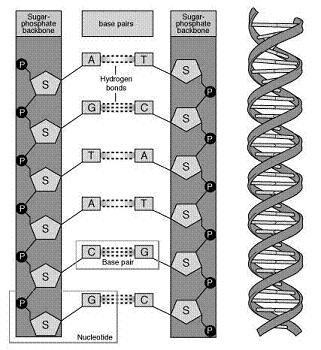 Inside each cell the DNA molecule is packaged into thread-like structures called chromosomes. Each chromosome is made up of DNA tightly coiled many times around proteins called histones that support its structure. 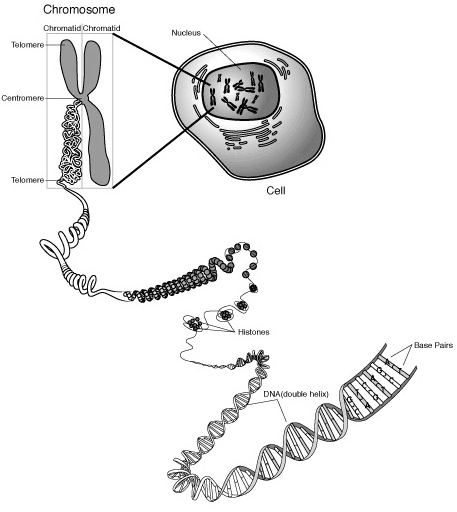 In humans, each cell normally contains 23 pairs of chromosomes, for a total of 46. Twenty-two of these pairs look the same in both males and females. The 23rd pair, the sex chromosomes, differ between males and females. Females have two copies of the X chromosome, while males have one X and one Y chromosome. A gene is basically a piece of the DNA string and is located on one of the chromosomes. It can be defined as a region of DNA that controls one hereditary characteristic. Genes act as instructions to make molecules called proteins. These proteins are large, complex molecules that play many critical roles in the body. They are required for the structure, function and regulation of the body's tissue and organs. The human body has between 20.000 and 25.000 genes and their size varies from a few hundred DNA bases to more than 2 million bases. Changes in the DNA sequence that make up a gene are called mutations. These mutations are often the cause for inherited disorders. Read further about the MCAD mutation >
|
||||
|
|
This page was last modified on 5 March 2011 | |||